


Flexible DC transmission has emerged as a prominent research focus in both academic and engineering circles, with its applications expanding rapidly. As core components of flexible DC systems, secondary control and protection equipment must undergo rigorous factory testing before deployment in practical projects. However, conventional testing methods only inspect routine aspects like product appearance and electrical insulation, failing to verify control and protection functions under near-real-world conditions. To address this limitation, a virtual grid environment must be created to integrate actual control and protection devices. This environment must simulate both steady-state characteristics of MMC-HVDC systems (such as startup, deblocking, and power transmission) and transient characteristics (including voltage sags, AC/DC faults, and valve body and submodule faults). Simulating these operational scenarios enables comprehensive validation of secondary control and protection equipment and helps manufacturers modify and optimize product performance.
Based on its years of technological accumulation, KeLiang has provided comprehensive simulation testing systems for research in flexible DC transmission (MMC-HVDC) technology to major domestic universities, research institutes, and enterprises. As one of the earliest commercial platforms with MMC real-time simulation capabilities, RT-LAB has played a important role in the R&D, functional testing, and optimization of control and protection devices for practical flexible DC engineering projects through its real-time simulation and hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing capabilities.
In the real-time simulation model, the main circuit of the MMC-HVDC system is computed on the CPU with a simulation step size of 20–50 μs, while the valve section is modeled and calculated on the OP7020 FPGA simulator at a step size of 500 ns. With communication protocols integrated, a single OP7020 can simulate up to 3,000 MMC submodules and connect to the valve control unit via optical fibers. Concurrently, the CPU interfaces with the control and protection devices through I/O ports, thereby forming a closed-loop hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulation system.
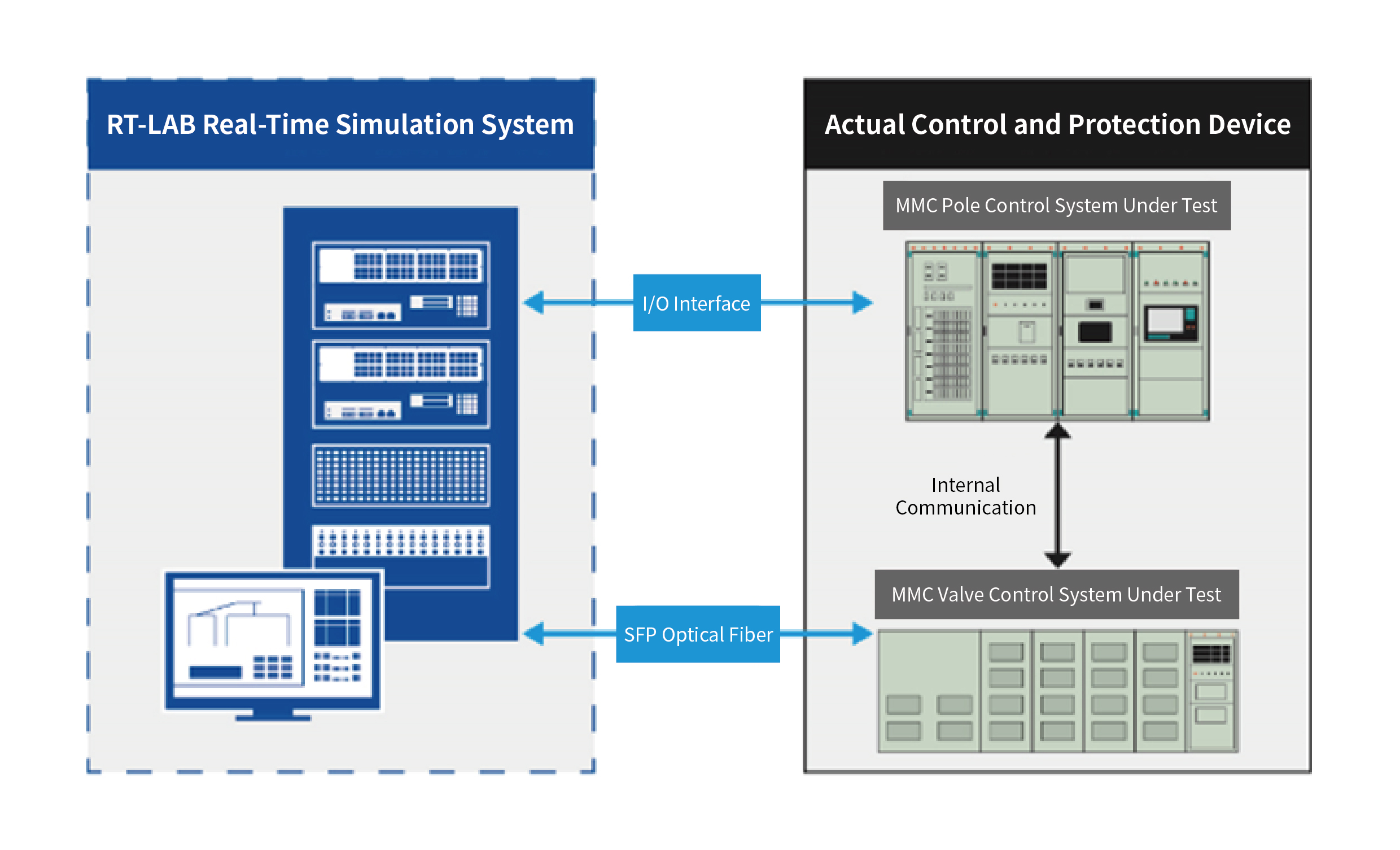
Fig.1 MMC-HVDC real-time simulation system
The MMC-HVDC simulation & testing system comprises the simulation software RT-LAB, simulation hardware OP5600 simulator, OP7020 simulator, network system, user workstation, and input/output interface devices.
Composition description of each part of the system:
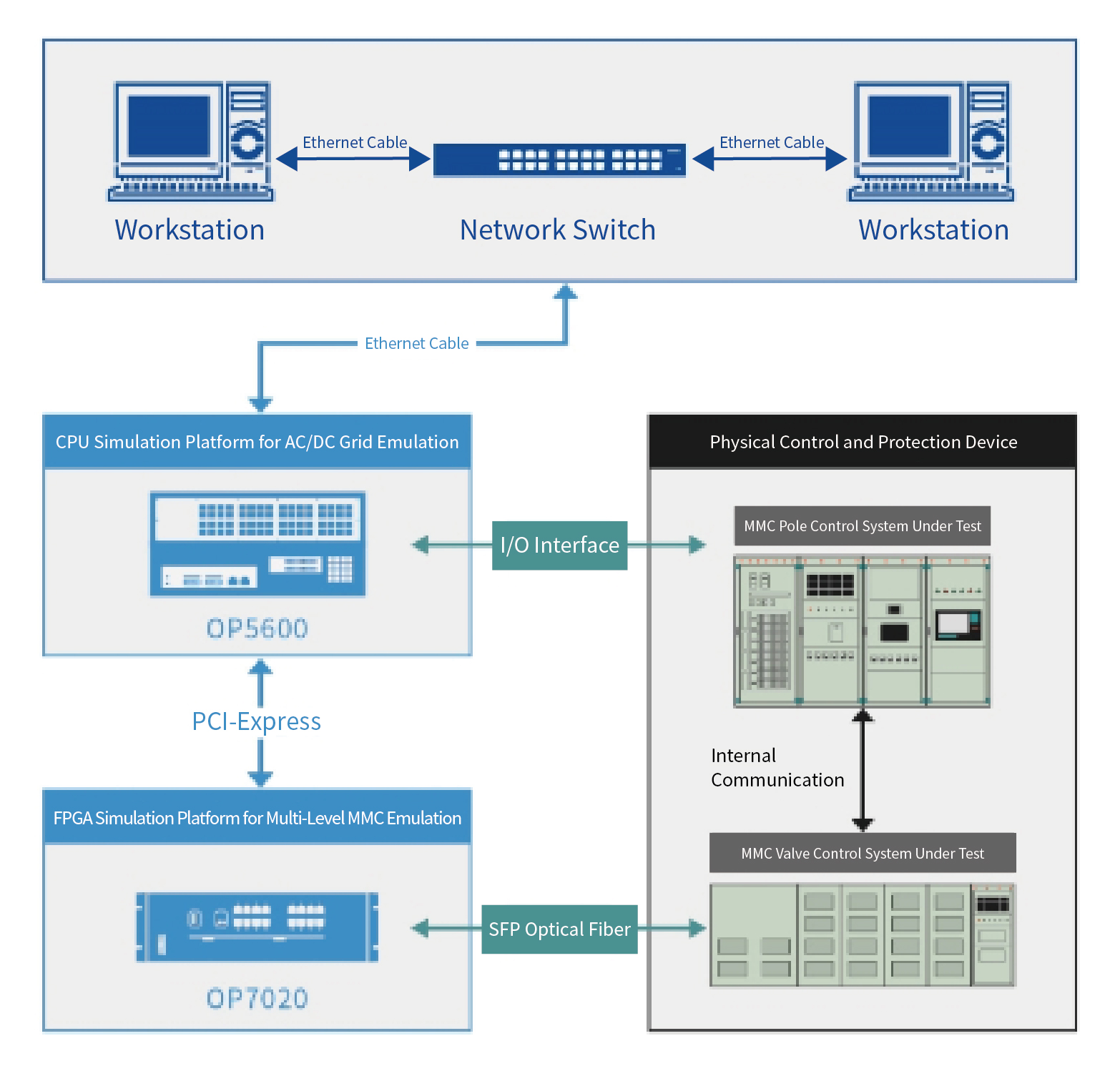
Fig.2 Composition of MMC-HVDC real-time simulation system
■ Eliminating design flaws in the early stages of valve control devices;
■ Cooperating with control protection devices to complete comprehensive system testing and validation;
■ Providing technical support for post-commissioning operation and maintenance, ensuring reliable operation after project commissioning.
This system enables the following tests on MMC-HVDC control protection and valve control devices:
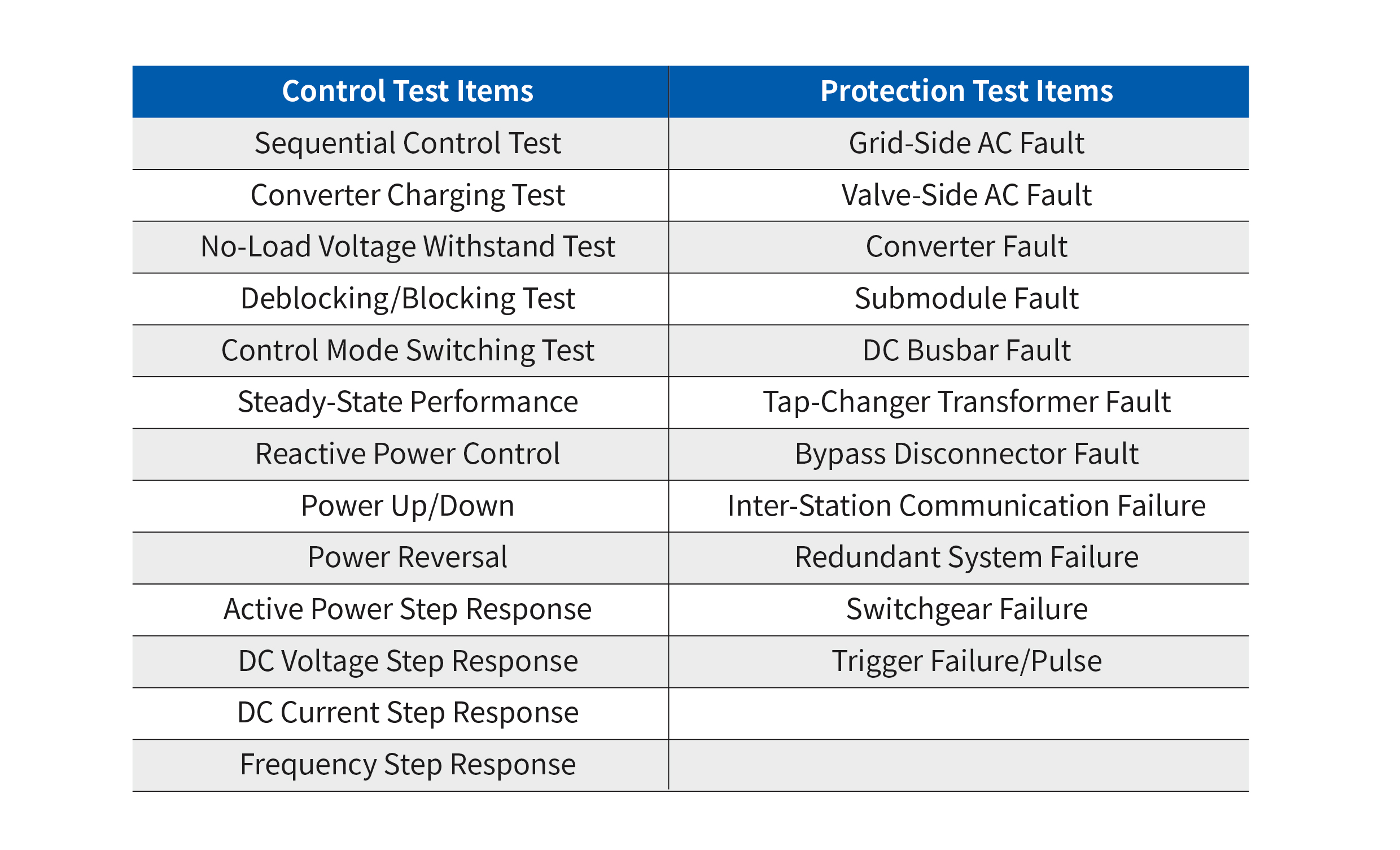
■ Electromagnetic transient simulation for AC/DC grids;
■ Real-time parallel computing technology using CPU and FPGA;
■ MMC valve models including half-bridge, full-bridge, clamped double, and hybrid HB-FB submodules;
■ FPGA enables simulation of converters with up to 1,024 cascaded MMC submodules per arm;
■ Apply semi-physical simulation technology to conduct FPT and DPT tests on flexible DC transmission control and protection equipment, including valve-based controllers;
■ Support for user-defined interface protocols.